Earthing & Earth Grid Design

Earthing and earth grid design is the process of designing, installing, and maintaining an earthing system that provides a low-impedance path for fault currents and lightning currents to flow safely to the ground. Earthing and grid design is important for ensuring the correct operation, safety, and protection of electrical equipment and people.
Some of the important aspects of earthing design are:
- The type of earthing system, which defines the relationship between the earth and the power supply neutral. There are different types of earthing systems, such as TN, TT, IT, etc., each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of earthing system depends on various factors, such as the supply system, the load characteristics, the fault level, the safety requirements, etc
- The earthing electrode is the part of the earthing system that is in contact with the soil. The earthing electrode should have a low resistance to earth and a large surface area to dissipate the fault currents or lightning currents effectively. The earthing electrode can be made of different materials, shapes, and sizes, such as rods, plates, tapes, wires, meshes, etc. The choice of earthing electrode depends on various factors, such as the soil resistivity, the moisture content, the corrosion potential, the installation depth, etc
- The earthing conductor, is the part of the earthing system that connects the earthing electrode to the equipment or structure to be earthed. The earthing conductor should have a low resistance and a high current-carrying capacity to avoid overheating or melting during fault conditions. The earthing conductor can be made of different materials, such as copper, aluminium, steel, etc., each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of earthing conductor depends on various factors, such as the current rating, the environmental conditions, the mechanical strength, etc
- The earthing design calculations are used to determine the optimal parameters and specifications of the earthing system components. The earthing design calculations involve various methods and formulas to estimate the earth resistance, the earth potential rise, the touch and step voltages, the fault current distribution, etc. The earthing design calculations should follow the relevant standards and codes of practice, such as IEC 60364-5-54, AS/NZS 3000:2018, IEEE Std 80-2013, AS/NZS 3007 etc.
Cell has a number of specialist in-house testing equipment including:
- Earthing Meggar and test kit
- Off Frequency injection test facility for earthing and step/touch potential generation and measurement.
- Power Quality Meters
Earth Grid Design Frequently Asked Questions:
An earth grid design involves various steps, such as performing soil resistivity measurements, selecting the type, size and layout of the earth conductors, calculating the earth resistance, the earth potential rise, the touch and step voltages, etc. The earth’s grid design should follow the relevant standards and codes of practice, such as AS 2067, IEEE Std 80, etc. The earth grid design should also consider the impact of the installation on nearby third-party assets, such as pipelines, railways, communication cables, etc.
An earth grid is a network of buried conductors that forms part of the earthing system of a substation, power station, wind farm or other electrical installation. It provides a low impedance path for fault currents and lightning currents to flow safely to the ground. It also helps to reduce the touch and step voltages within and around the installation, thereby protecting people and equipment from electric shock
AS2067 offers the following design guidelines for earth grid construction as follows:
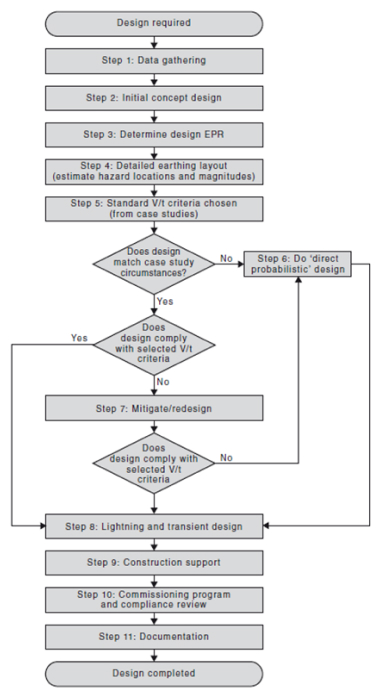
The performance of an earth grid depends on various factors, such as the soil resistivity, the moisture content, the temperature, the corrosion potential, the fault current level and duration, the frequency of the current, the geometry and material of the earth conductors, the connection and jointing methods, etc. These factors should be taken into account in the earth grid design and maintenance.
An earth grid should be tested and maintained regularly to ensure its functionality and safety. The testing methods include resistance testing, continuity testing, ground or soil resistivity testing and visual inspection. The testing results should be compared with the design specifications and any deviations or defects should be rectified. The maintenance activities include cleaning, tightening, repairing or replacing any damaged or corroded components of the earth grid. Other considerations for earth grids are step and touch and Cell also recommends that a regular inspection and test plan be developed to ensure the system is operating effectively. This is typically an annual test via off-frequency injection test equipment.



